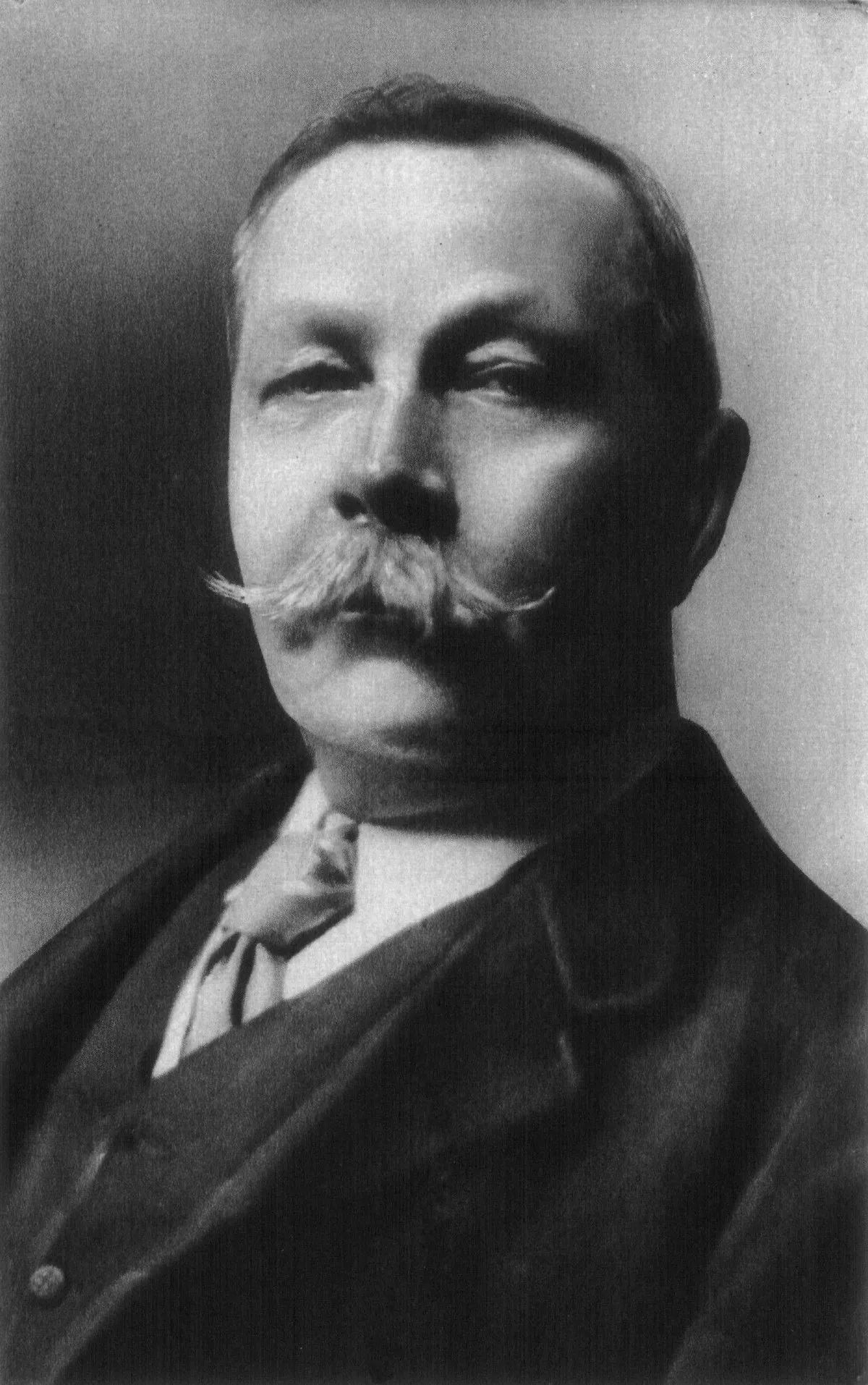 1.
1. Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle was a British writer and physician.
 1.
1. Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle was a British writer and physician.
Arthur Conan Doyle created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for A Study in Scarlet, the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Holmes and Dr Watson.
Arthur Conan Doyle was born on 22 May 1859 at 11 Picardy Place, Edinburgh, Scotland.
Arthur Conan Doyle's father, Charles Altamont Doyle, was born in England, of Irish Catholic descent, and his mother, Mary, was Irish Catholic.
Arthur Conan Doyle lodged with Mary Burton, the aunt of a friend, at Liberton Bank House on Gilmerton Road, while studying at Newington Academy.
Arthur Conan Doyle's father died in 1893, in the Crichton Royal, Dumfries, after many years of psychiatric illness.
Arthur Conan Doyle went on to Stonyhurst College, which he attended until 1875.
Arthur Conan Doyle commented later in his life that this academic system could be excused only "on the plea that any exercise, however stupid in itself, forms a sort of mental dumbbell by which one can improve one's mind".
Arthur Conan Doyle found the school harsh, noting that, instead of compassion and warmth, it favoured the threat of corporal punishment and ritual humiliation.
Arthur Conan Doyle's family decided that he would spend a year there in order to perfect his German and broaden his academic horizons.
Arthur Conan Doyle was raised Catholic but later rejected the faith and became an agnostic.
From 1876 to 1881, Arthur Conan Doyle studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh Medical School; during this period he spent time working in Aston, Sheffield and Ruyton-XI-Towns, Shropshire.
Arthur Conan Doyle's first published piece, "The Mystery of Sasassa Valley", a story set in South Africa, was printed in Chambers's Edinburgh Journal on 6 September 1879.
Arthur Conan Doyle was the doctor on the Greenland whaler Hope of Peterhead in 1880.
In 1882, Arthur Conan Doyle partnered with his former classmate George Turnavine Budd in a medical practice in Plymouth, but their relationship proved difficult, and Arthur Conan Doyle soon left to set up an independent practice.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a staunch supporter of compulsory vaccination and wrote several articles advocating the practice and denouncing the views of anti-vaccinators.
In early 1891, Arthur Conan Doyle embarked on the study of ophthalmology in Vienna.
Arthur Conan Doyle had previously studied at the Portsmouth Eye Hospital in order to qualify to perform eye tests and prescribe glasses.
Arthur Conan Doyle opened a small office and consulting room at 2 Upper Wimpole Street, or 2 Devonshire Place as it was then.
Arthur Conan Doyle felt grievously exploited by Ward Lock as an author new to the publishing world, and so, after this, he left them.
Arthur Conan Doyle wrote the first five Holmes short stories from his office at 2 Devonshire Place.
In December 1893, to dedicate more of his time to his historical novels, Arthur Conan Doyle had Holmes and Professor Moriarty plunge to their deaths together down the Reichenbach Falls in the story "The Final Problem".
Between 1888 and 1906, Arthur Conan Doyle wrote seven historical novels, which he and many critics regarded as his best work.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a prolific author of short stories, including two collections set in Napoleonic times and featuring the French character Brigadier Gerard.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a keen cricketer, and between 1899 and 1907 he played 10 first-class matches for the Marylebone Cricket Club.
In 1900, Arthur Conan Doyle founded the Undershaw Rifle Club at his home, constructing a 100-yard range and providing shooting for local men, as the poor showing of British troops in the Boer War had led him to believe that the general population needed training in marksmanship.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a champion of "miniature" rifle clubs, whose members shot small-calibre firearms on local ranges.
Arthur Conan Doyle went on to sit on the Rifle Clubs Committee of the National Rifle Association.
In 1901, Arthur Conan Doyle was one of three judges for the world's first major bodybuilding competition, which was organised by the "Father of Bodybuilding", Eugen Sandow.
Also a keen golfer, Arthur Conan Doyle was elected captain of the Crowborough Beacon Golf Club in Sussex for 1910.
Arthur Conan Doyle had moved to Little Windlesham house in Crowborough with Jean Leckie, his second wife, and resided there with his family from 1907 until his death in July 1930.
Arthur Conan Doyle entered the English Amateur billiards championship in 1913.
Arthur Conan Doyle wrote an article, "An Alpine Pass on 'Ski" for the December 1894 issue of The Strand Magazine, in which he described his experiences with skiing and the beautiful alpine scenery that could be seen in the process.
In 1885 Arthur Conan Doyle married Louisa Hawkins.
Arthur Conan Doyle was the youngest daughter of J Hawkins, of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, and the sister of one of Doyle's patients.
Arthur Conan Doyle had met and fallen in love with Jean in 1897, but had maintained a platonic relationship with her while his first wife was still alive, out of loyalty to her.
Arthur Conan Doyle had two with his first wife: Mary Louise and Arthur Alleyne Kingsley, known as Kingsley.
Arthur Conan Doyle had an additional three with his second wife: Denis Percy Stewart, who became the second husband of Georgian Princess Nina Mdivani; Adrian Malcolm ; and Jean Lena Annette.
Arthur Conan Doyle served as a volunteer physician in the Langman Field Hospital at Bloemfontein between March and June 1900, during the Second Boer War in South Africa.
The latter work was widely translated, and Arthur Conan Doyle believed it was the reason he was knighted by King Edward VII in the 1902 Coronation Honours.
Arthur Conan Doyle stood for Parliament twice as a Liberal Unionist: in 1900 in Edinburgh Central, and in 1906 in the Hawick Burghs, but was not elected.
Arthur Conan Doyle served as a Deputy-Lieutenant of Surrey beginning in 1902, and was appointed a Knight of Grace of the Order of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem in 1903.
Arthur Conan Doyle became acquainted with Morel and Casement, and it is possible that, together with Bertram Fletcher Robinson, they inspired several characters that appear in his 1912 novel The Lost World.
Arthur Conan Doyle tried, unsuccessfully, to save him, arguing that Casement had been driven mad, and therefore should not be held responsible for his actions.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a fervent advocate of justice and personally investigated two closed cases, which led to two men being exonerated of the crimes of which they were accused.
Apart from helping George Edalji, Arthur Conan Doyle's work helped establish a way to correct other miscarriages of justice, as it was partially as a result of this case that the Court of Criminal Appeal was established in 1907.
Arthur Conan Doyle ended up paying most of the costs for Slater's successful 1928 appeal.
Arthur Conan Doyle had a longstanding interest in mystical subjects and remained fascinated by the idea of paranormal phenomena, even though the strength of his belief in their reality waxed and waned periodically over the years.
In 1887, in Southsea, influenced by Major-General Alfred Wilks Drayson, a member of the Portsmouth Literary and Philosophical Society, Arthur Conan Doyle began a series of investigations into the possibility of psychic phenomena and attended about 20 seances, experiments in telepathy, and sittings with mediums.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a member of the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn.
Arthur Conan Doyle praised the psychic phenomena and spirit materialisations that he believed had been produced by Eusapia Palladino and Mina Crandon, both of whom were later exposed as frauds.
Arthur Conan Doyle wrote a piece in Light magazine about his faith and began lecturing frequently on spiritualism.
Arthur Conan Doyle found solace in supporting spiritualism's ideas and the attempts of spiritualists to find proof of an existence beyond the grave.
Arthur Conan Doyle was a member of the supernaturalist organisation The Ghost Club.
Arthur Conan Doyle debated the psychiatrist Harold Dearden, who vehemently disagreed with Arthur Conan Doyle's belief that many cases of diagnosed mental illness were the result of spirit possession.
In 1920, Arthur Conan Doyle travelled to Australia and New Zealand on spiritualist missionary work, and over the next several years, until his death, he continued his mission, giving talks about his spiritualist conviction in Britain, Europe, and the United States.
Arthur Conan Doyle wrote a novel The Land of Mist centred on spiritualist themes and featuring the character Professor Challenger.
Arthur Conan Doyle was friends for a time with the American magician Harry Houdini.
However, according to Ernst, Arthur Conan Doyle simply refused to believe that it had been a trick.
Arthur Conan Doyle insisted that spiritualist mediums employed trickery, and consistently exposed them as frauds.
Arthur Conan Doyle defended Hope, but further evidence of trickery was obtained from other researchers.
Arthur Conan Doyle threatened to have Price evicted from the National Laboratory of Psychical Research and predicted that, if he persisted in writing what he called "sewage" about spiritualists, he would meet the same fate as Harry Houdini.
In 1927, Arthur Conan Doyle gave a filmed interview, in which he spoke about Sherlock Holmes and spiritualism.
Samuel Rosenberg's 1974 book Naked Is the Best Disguise purports to explain how, throughout his writings, Arthur Conan Doyle had provided overt clues to otherwise hidden or suppressed aspects of his way of thinking that seemed to support the idea that Arthur Conan Doyle would be involved in such a hoax.
However, more recent research suggests that Arthur Conan Doyle was not involved.
Arthur Conan Doyle wanted to be a member of the Royal Society and he was after an MBE [sic].
The home in which he lived from October 1897 to September 1907, known as Undershaw, was used as a hotel and restaurant from 1924 until 2004, when it was bought by a developer and then stood empty while conservationists and Arthur Conan Doyle fans fought to preserve it.
Arthur Conan Doyle made his most ambitious foray into architecture in March 1912, while he was staying at the Lyndhurst Grand Hotel: he sketched the original designs for a third-storey extension and for an alteration of the front facade of the building.
In 1926, Arthur Conan Doyle laid the foundation stone for a Spiritualist Temple in Camden, London.
Arthur Conan Doyle was found clutching his chest in the hall of Windlesham Manor, his house in Crowborough, Sussex, on 7 July 1930.
Arthur Conan Doyle died of a heart attack at the age of 71.
Arthur Conan Doyle was first buried on 11 July 1930 in Windlesham rose garden.
Arthur Conan Doyle was later reinterred together with his wife in Minstead churchyard in the New Forest, Hampshire.
Arthur Conan Doyle has been commemorated with statues and plaques since his death.
Arthur Conan Doyle has been portrayed by many actors, including:.
Arthur Conan Doyle is the ostensible narrator of Ian Madden's short story "Cracks in an Edifice of Sheer Reason".