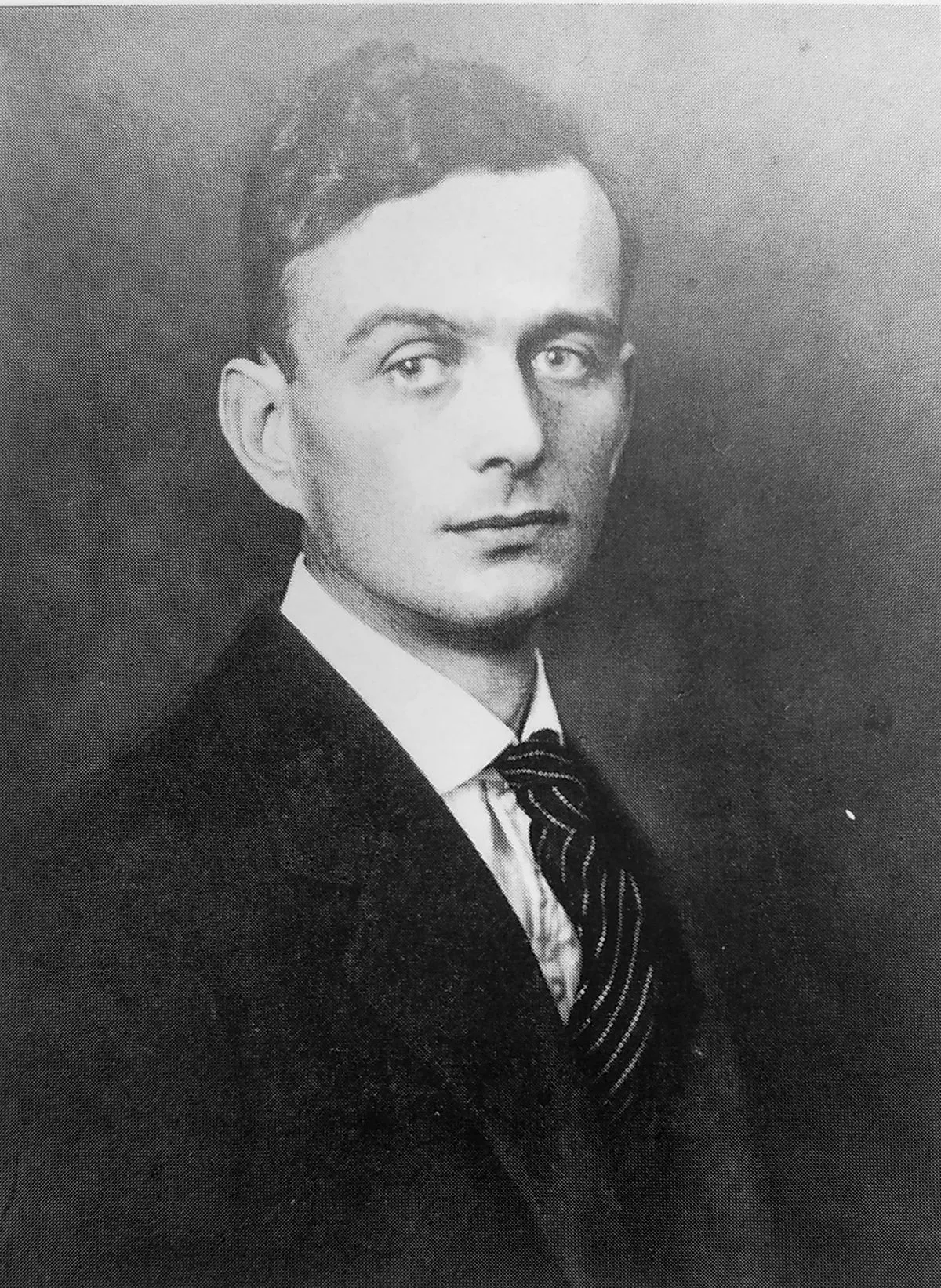 1.
1. Erwin Friedrich Theodor Stresemann was a German naturalist and ornithologist.
 1.
1. Erwin Friedrich Theodor Stresemann was a German naturalist and ornithologist.
Erwin Stresemann influenced numerous ornithologists around him and oversaw the development of ornithology in Germany as editor of the Journal fur Ornithologie.
Erwin Stresemann took an interest in poetry, philosophy and linguistics.
Erwin Stresemann published a monograph on the Paulohi language based on studies made during his ornithological expedition to the Indonesian island.
Erwin Stresemann was born in Dresden to Richard, an apothecary and Marie.
Erwin Stresemann made contact with Ernst Haeckel and studied marine biology at Bergen.
Erwin Stresemann took a break from 1910 to 1912 to join as an ornithologist the "Second Freiburg Expedition" to the Moluccas.
The cost had to be borne by the participants, and Erwin Stresemann prepared himself on fauna, geology and ethnology of the Moluccas.
Erwin Stresemann went to Tring and consulted with Ernst Hartert and then climbed hills and trained to stand the heat by climbing Mount Vesuvius.
Erwin Stresemann spent six months studying the language and exploring Buru.
Erwin Stresemann then studied the bird collections at the Rothschild Museum in Tring where Ernst Hartert worked.
Erwin Stresemann's study was supported by Rothschild, and several new species were named in his honour.
Erwin Stresemann published his studies on the now near-extinct Paulohi language and wrote a monograph on the topic and a paper on language relations.
Erwin Stresemann took an interest in poetry, the writings of Goethe, Descartes and Bismarck.
Erwin Stresemann's studies were interrupted by the First World War and he was conscripted, serving initially in an artillery unit on the Western Front.
Erwin Stresemann was transferred to Italy and was wounded in November 1917.
Erwin Stresemann returned to Munich and resumed his studies and graduated with majors in zoology and minors in botany and anthropology.
Erwin Stresemann briefly studied under Richard von Hertwig in Munich and examined the avifauna of Macedonia.
The Aves work continued to be updated until 1934 and Erwin Stresemann produced one of the most comprehensive treatises on birds.
Erwin Stresemann attended meetings of the Deutsche Ornithologen-Gesellschaft where he was known for his argumentation.
Erwin Stresemann proved himself as a person of wide reading and immense knowledge.
Erwin Stresemann was made professor in 1930 and from 1946 to 1961 he was tenured professor at the Humboldt University of Berlin.
In November 1935, Erwin Stresemann was invited to Yale University by Leonard Cutler Sanford and was offered a position there.
Erwin Stresemann wrote that he could have worked there but could not live there.
Erwin Stresemann kept up communication with European ornithologists who became German prisoners of war such as David Bannerman.
Erwin Stresemann ensured that they obtained the latest research papers as well.
Erwin Stresemann found several other biological traits that seemed to influence moult, at least of the flight feathers.
Erwin Stresemann was decorated with GDR Patriotic Order of Merit.
Erwin Stresemann was one of the outstanding ornithologists of the 20th century but is often not recognized outside Germany because most of his works were written in German and ignored due to the wartime rivalries.
At the age of 40, Erwin Stresemann was elected President of the 8th International Congress.
Erwin Stresemann was the long-standing editor of the Journal fur Ornithologie.
Erwin Stresemann wrote Entwicklung der Ornithologie von Aristoteles bis zur Gegenwart, a review of the development of ornithology from Aristotle to modern times, translated into English in 1975 as "Ornithology from Aristotle to the Present".
Erwin Stresemann married Elisabeth Deninger, sister of his expedition-mate Karl Deninger, in 1916.
Erwin Stresemann was the daughter of chemist Albert Deninger, known for his work on fluoride toothpastes.
Erwin Stresemann married Vesta nee Grote during the war years in 1941 and they worked on many ornithological papers, especially on moult, and she survived him to live to 103 years.
Erwin Stresemann was known for his impeccable sense of dressing, his affable personality and excellent dancing in his youth.
Erwin Stresemann was an excellent speaker, carefully adding wit and humour, and proud of the German language despite knowing excellent English.
Erwin Stresemann died after suffering from poor health since his 80th birthday.
Erwin Stresemann however suffered that autumn with a heart-trouble and he had wished to be buried alongside his mentor Ernst Hartert.
Erwin Stresemann was cremated and according to his wishes the ashes were interred into the grave of Ernst Hartert in the Waldfriedhof at Dahlem.
Erwin Stresemann however supported British prisoners of war including John Buxton, Peter Conder, and George Waterston in Nazi Germany who were interested in birds, providing them books and supporting their bird studies.