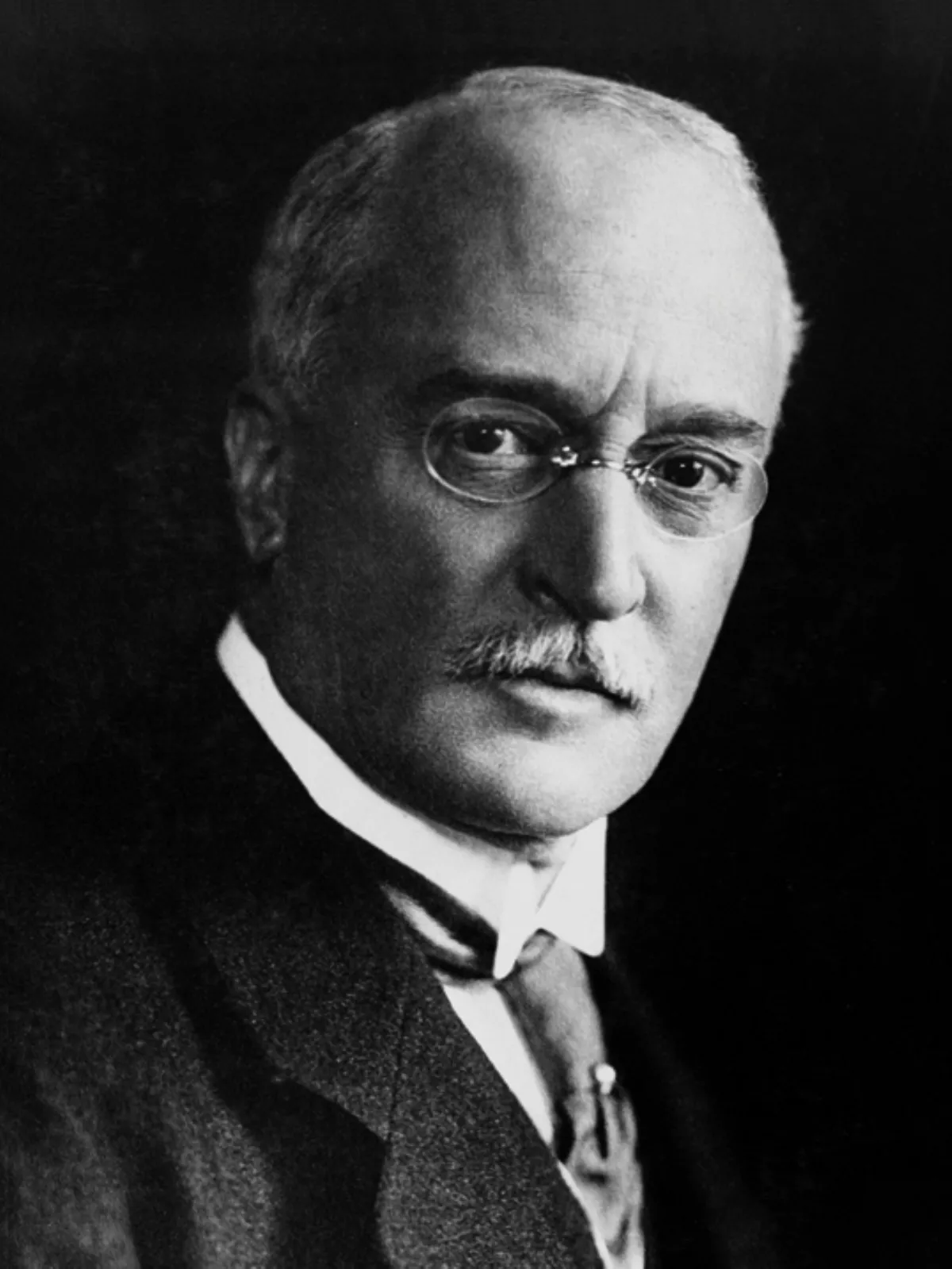 1.
1. Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.
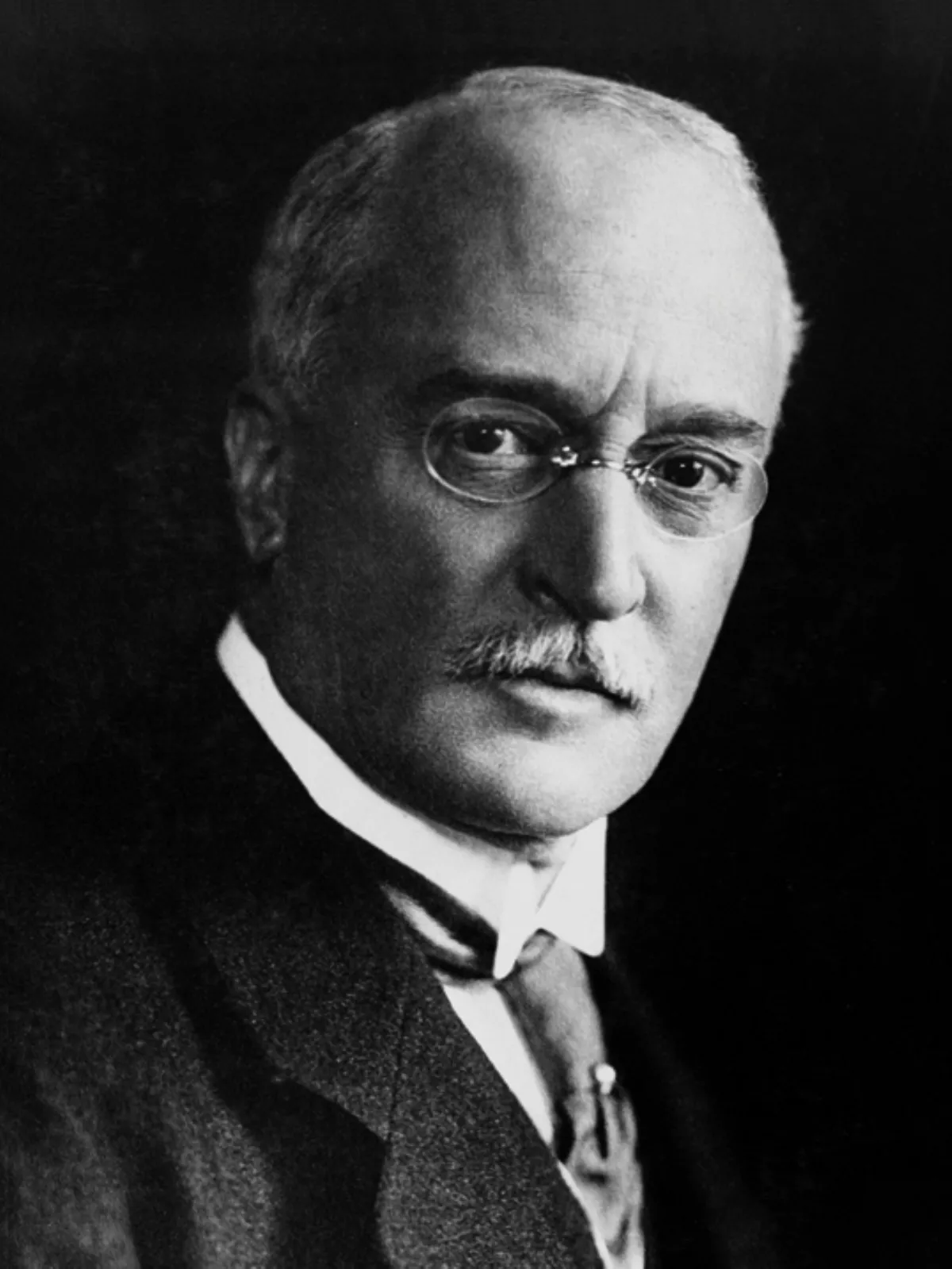
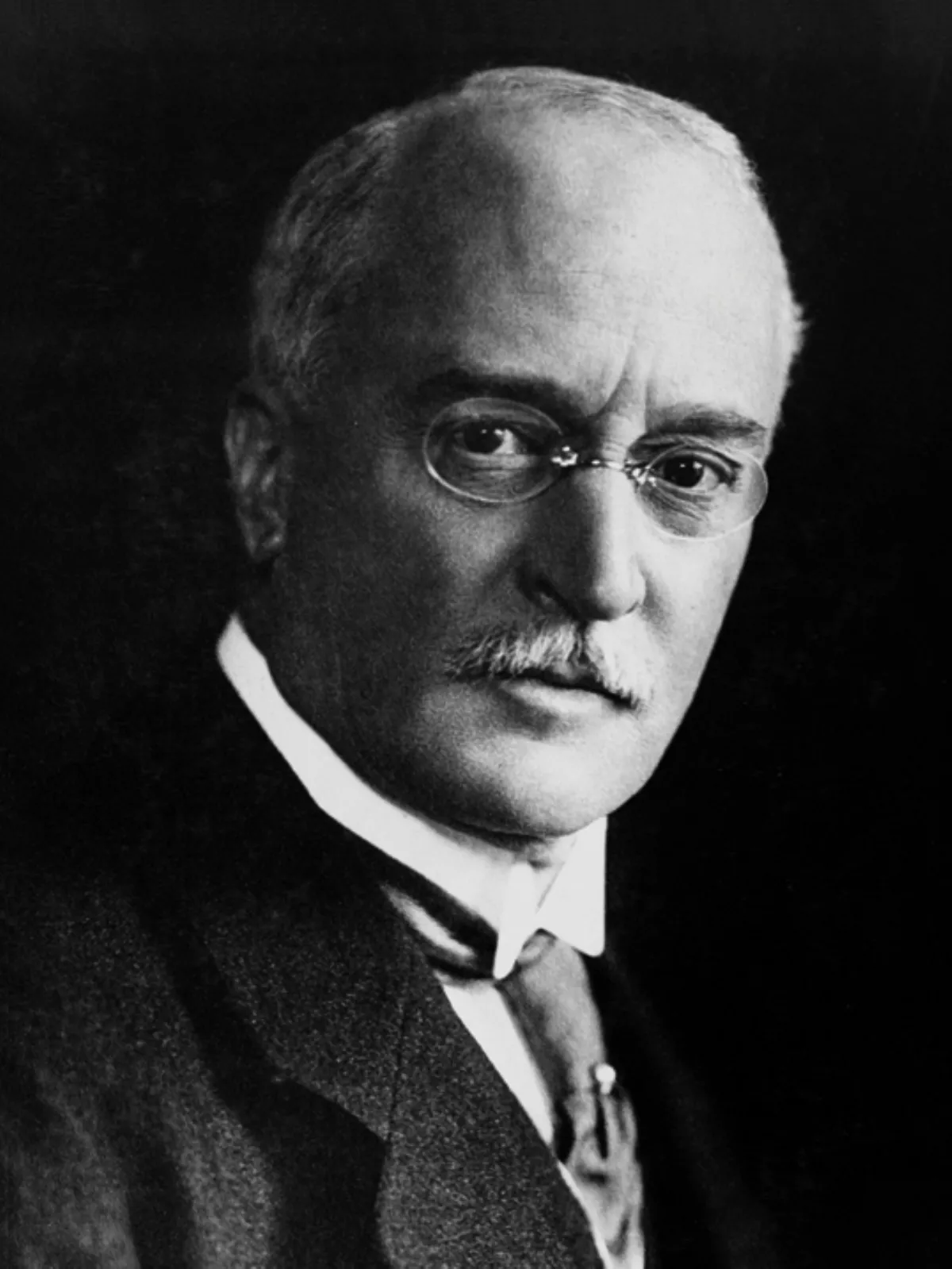 1.
1. Rudolf Christian Karl Diesel was a German inventor and mechanical engineer who invented the Diesel engine, which burns Diesel fuel; both are named after him.
Rudolf Diesel met his wife, a daughter of a Nuremberg merchant, in Paris in 1855 and became a leather goods manufacturer there.
Shortly after his birth, Rudolf Diesel was given away to a Vincennes farmer family, where he spent his first nine months.
At the time, the Diesel family suffered from financial difficulties, thus young Rudolf Diesel had to work in his father's workshop and deliver leather goods to customers using a barrow.
Rudolf Diesel attended a Protestant-French school and soon became interested in social questions and technology.
At the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War the same year, his family were deported to England, settling in London, where Rudolf Diesel attended an English-speaking school.
Rudolf Diesel was enrolled at the Technische Hochschule.
At the age of 14, Rudolf Diesel wrote a letter to his parents saying that he intended to become an engineer.
Rudolf Diesel was unable to graduate with his class in July 1879 because he fell ill with typhoid fever.
Rudolf Diesel graduated in January 1880 with highest academic honours and returned to Paris, where he assisted Linde with the design and construction of a modern refrigeration and ice plant.
Rudolf Diesel became the director of the plant a year afterwards.
In 1883, Rudolf Diesel married Martha Flasche, and continued to work for Linde, gaining numerous patents in both Germany and France.
Rudolf Diesel first worked with steam, his research into thermal efficiency and fuel efficiency leading him to build a steam engine using ammonia vapor.
Rudolf Diesel spent many months in a hospital, followed by health and eyesight problems.
Ever since attending lectures of von Linde, Rudolf Diesel worked on designing an internal combustion engine that could approach the maximum theoretical thermal efficiency of the Carnot cycle.
Rudolf Diesel understood thermodynamics and the theoretical and practical constraints on fuel efficiency.
Rudolf Diesel's design utilised compression ignition as opposed to using spark plugs similar to gas engines, with the ability to be run on biodiesel, if not petroleum-originating fuels.
Besides Germany, Rudolf Diesel obtained patents for his design in other countries, including the United States.
Rudolf Diesel was inducted into the Automotive Hall of Fame in 1978.
Rudolf Diesel discovered 20,000 German marks in cash and financial statements indicating that their bank accounts were virtually empty.
Yamaoka and people associated with Rudolf Diesel began to make preparations to honour him.
However, the Rudolf Diesel engine became widespread in many other applications, such as stationary engines, agricultural machines and off-highway machinery in general, submarines, ships, and much later, locomotives, trucks, and in modern automobiles.
Rudolf Diesel engines have the benefit of running more fuel-efficiently than any other internal combustion engines suited for motor vehicles, allowing more heat to be converted to mechanical work.
Rudolf Diesel was interested in using coal dust or vegetable oil as fuel, and in fact, his engine was run on peanut oil.
The primary fuel used in Rudolf Diesel engines is the eponymous diesel fuel, derived from the refinement of crude oil.