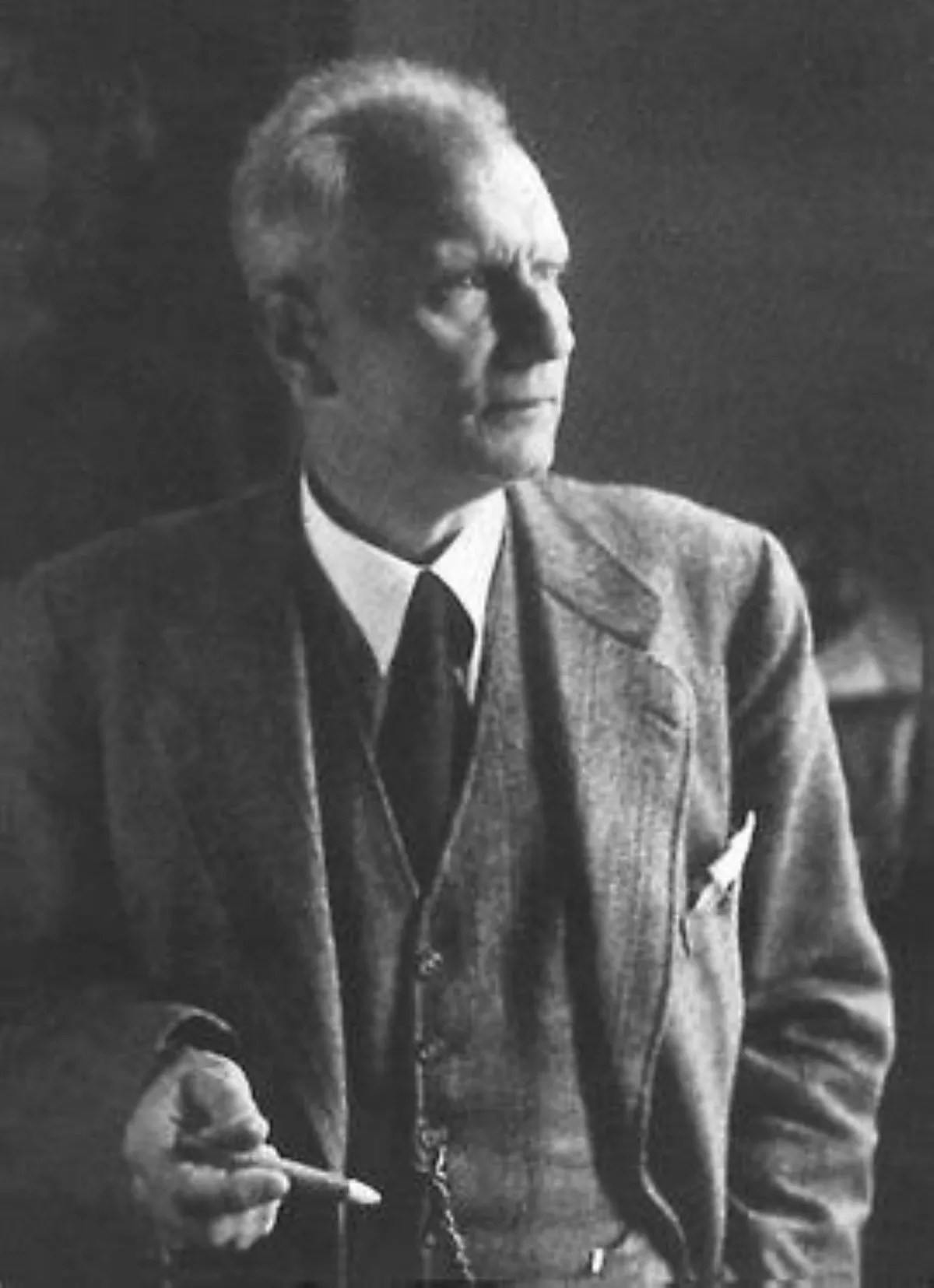 1.
1. Walther Gerlach was Nazi Germany's plenipotentiary of nuclear physics from December 1943 until his capture by US Army in May 1945.
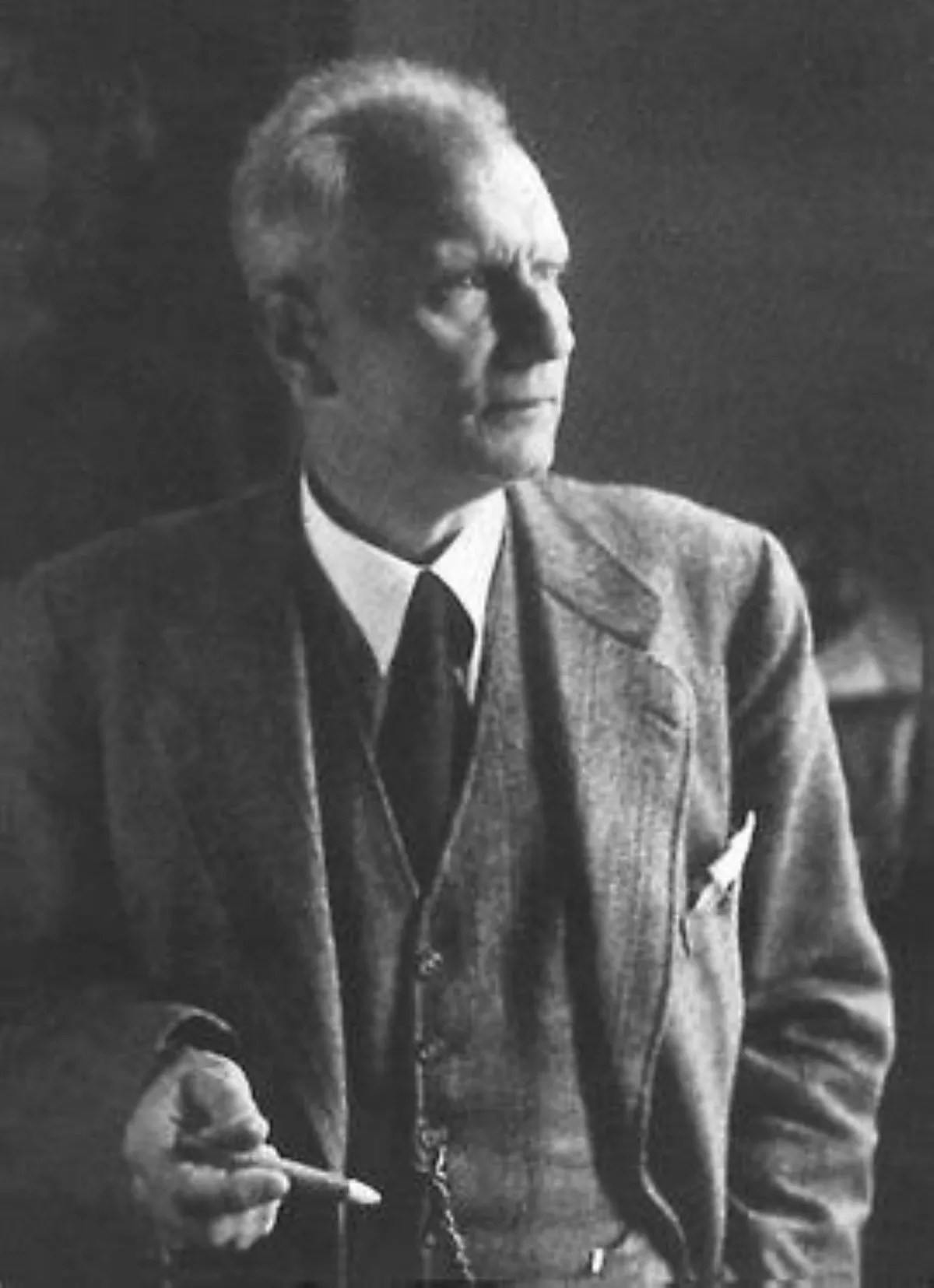
 1.
1. Walther Gerlach was Nazi Germany's plenipotentiary of nuclear physics from December 1943 until his capture by US Army in May 1945.
Walther Gerlach was born in Biebrich, Hessen-Nassau, German Empire, as son of Dr med.
Walther Gerlach studied at the University of Tubingen from 1908, and received his doctorate in 1912, under Friedrich Paschen.
From 1915 to 1918, during the war, Walther Gerlach did service with the German Army.
Walther Gerlach worked on wireless telegraphy at Jena under Max Wien.
Walther Gerlach became a Privatdozent at the University of Tubingen in 1916.
In 1925, Walther Gerlach took a call and became an ordinarius professor at the University of Tubingen, successor to Friedrich Paschen.
Walther Gerlach held this position until May 1945, when he was arrested by the American and British Armed Forces.
From 1937 until 1945, Walther Gerlach was a member of the supervisory board of the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Gesellschaft.
On 2 December 1943, on Mentzel's initiative, Walther Gerlach was appointed by the Reich Minister of Armaments and War Production Albert Speer as head of the physics section of the Reichsforschungsrat and as the plenipotentiary of nuclear physics, replacing Abraham Esau.
Walther Gerlach established himself with his deputy Kurt Diebner in the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics in Berlin-Dahlem.
Walther Gerlach is known to have worked in the uranium research laboratory in the basement of the secondary school at Stadtilm, where Diebner's team evacuated from Berlin in the autumn of 1944 and began to prepare a low-temperature experiment in a uranium machine without the use of heavy water.
Walther Gerlach himself was captured by the American troops in Bavaria by 12 May 1945.
Walther Gerlach was rector of the university from 1948 to 1951.
From 1949 to 1951, Walther Gerlach was the founding president of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, which promotes applied sciences.
In 1957, Walther Gerlach was a co-signer of the Gottingen Manifesto, which was against rearming the Federal Republic of Germany with atomic weapons.